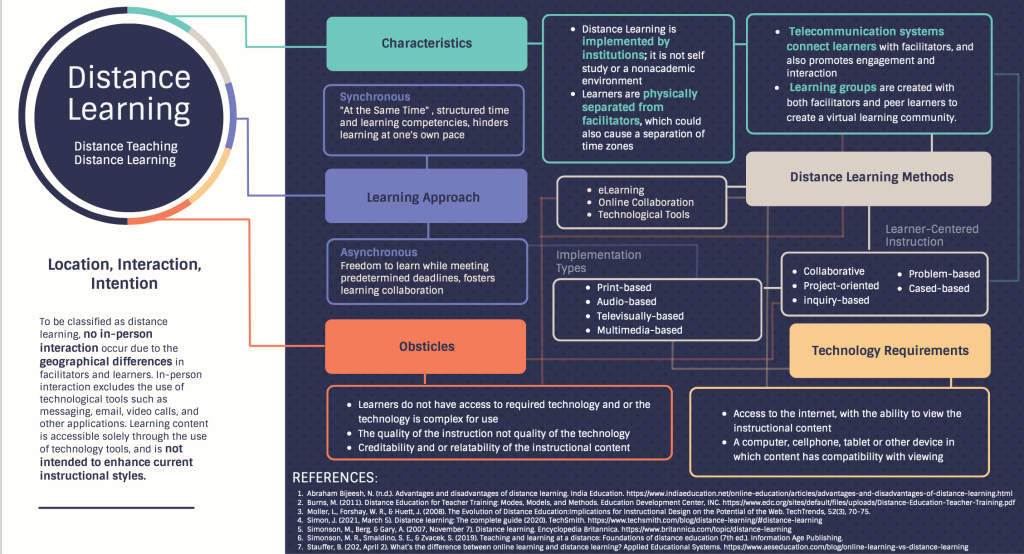
Past Experience
Acquiring new knowledge through distance learning has occurred in higher education and professional development. In both academics and corporate learning environments have migrated from in-person facilitation to online instruction through the integration of content management systems, CMS. Understanding of CMS was acquired in my previous degree, which specialized in the design and back-end development of the system. CMS offers instruction in which is accessible using various media viewers and multimedia elements such as audio and video (Simon, 2021). Overall, CMS provides a way to store and retrieve content that is both conveniently accessible and scalable.
In the corporate learning environment, I have seen an increase in online instructional content via eLearning modules. It seems as if eLearning has taking precedent over face-to-face instruction and the new preferred method of facilitation. The scalability and analytical data of a CMS demonstrate ROI through cost, increasing overall company profit (Stauffer, 2021). CMS offers a great solution to provide completion rates and formal assessment rankings; however, much of the learner’s information was not cognitively processed adequately for memory storage.
Current Experience
Using a CMS system does not ensure instruction is considered to be distance learning. Creating a virtual learning community where human collaboration is required to achieve learning goals within a CMS differentiates online instruction and distance learning. Distance learning is a facilitation method where instructors rely solely on technological advancements to group learners, without geographical restrictions, in a collaborative virtual environment (Simonson et al., 2019, p.33). Distance learning requires collaborative bi-directional communication to include the human aspect of learning, assessments, and feedback. An online eLearning module may yield positive learning assessments; however, the quality of learning and the ability to recall knowledge is negatively impacted if knowledge feedback is generalized or perceived as non-personal.
Communication tools in conjunction with a CMS, learners are provided with a platform to receive and provide real-time feedback. The amount of personalized feedback and the timeframe the feedback is given creates a humanized approach to online instruction. Humanizing instructional content allows learners to bridge the gap between knowledge and practical implementation and promotes cognitive processing needed for knowledge storage.
Vision
The current state of remote education has influenced growth in instructional technologies and platforms. More institutions are investing in mobile-friendly CMS to deliver real-time access to fluid content that includes virtual communication platforms. In the current pandemic state, distance learning has been brought to the forefront of facilitation methods. While adult learners are custom to virtual learning environments, challenges with learner engagement and environmental influences hinder younger learners.
Learning and development programs using distance learning methods must ensure learners are fully engaged in the instruction. Technology such as holograms and virtual reality offer solutions for controlling external environmental influences and engagement levels. Virtual reality offers an immersive learning experience, where each instructional scenario is conducted in a controlled and safe environment. Holograms in distance learning would not focus on the learning environment but a physical three-dimensional object in which learners create stronger connections between the instruction and real-world implementation. Both advancements would help generate engagement and foster motivation and excitement.
References
Simon, J. (2021, March 5). Distance learning: The complete guide (2020). TechSmith. https://www.techsmith.com/blog/distance-learning/#distance-learning
Simonson, M. R., Smaldino, S. E., & Zvacek, S. (2019). Teaching and learning at a distance: Foundations of distance education (7th ed.). Information Age Publishing.
Stauffer, B. (2021, April 2). What’s the difference between online learning and distance learning?Applied Educational Systems. https://www.aeseducation.com/blog/online-learning-vs-distance-learning

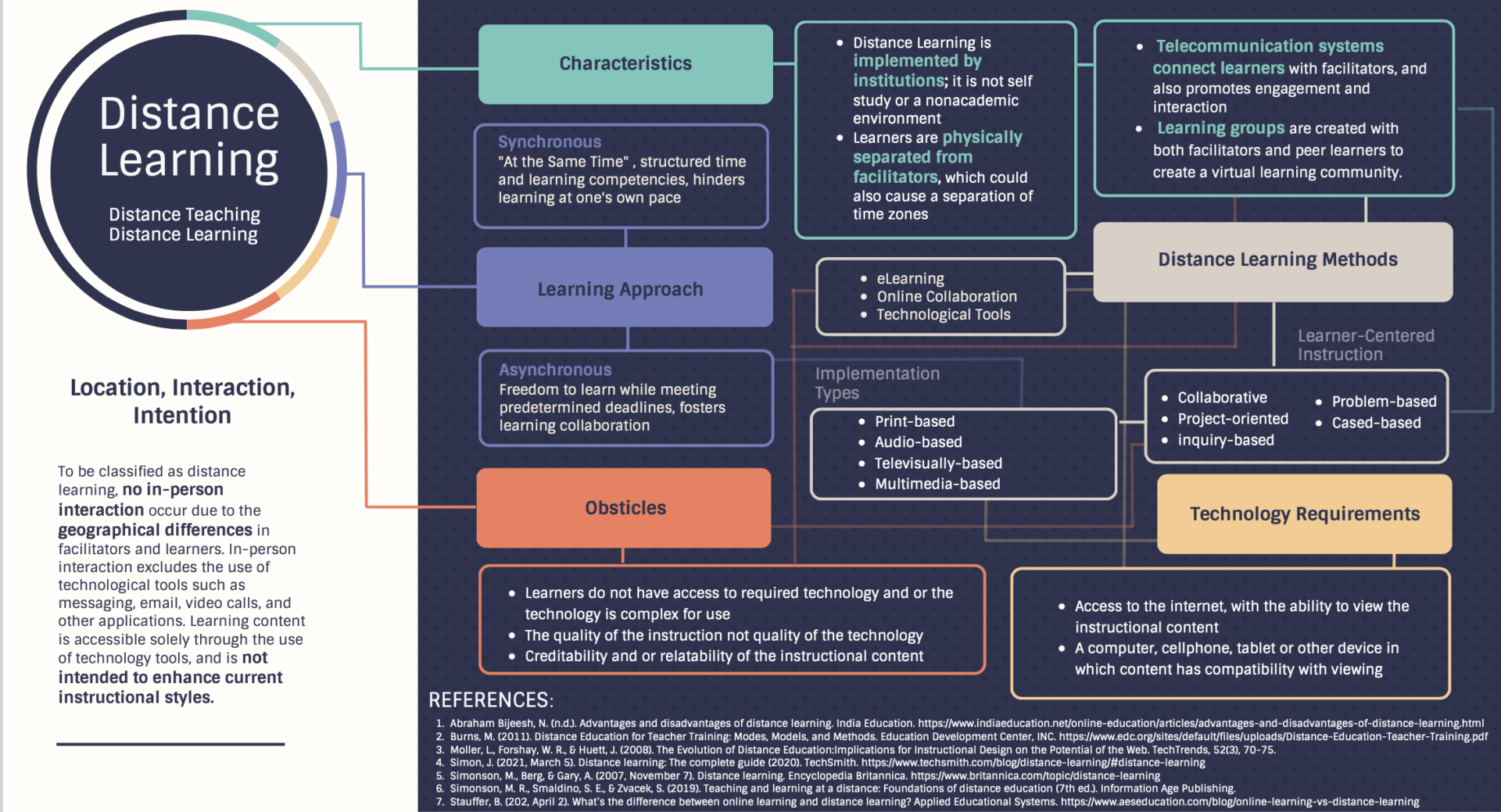
Nice organization! I would argue that distance learning also occurs in self-directed classes, like in MOOCs. It would be great to see more community building in distance learning classes, but I find that the instructor has to be proactive in facilitating such connections.